The first step in the process of assessing a patient involves collecting data that aids in diagnoses. These data could be heart rate, blood pressure, lab results and so on all recorded in numerical values, that are easy for health professionals to understand and identify patient physiology that is normal or abnormal, they are objective data, in fact, most health care professionals focus more on this information, however objective data alone is insufficient in patient assessment, it does not give a full picture of what the patient is going through. There are other data that cannot be measured or given numerical values but are critical points in patient assessment. They are subjective data.
Objective and subjective data are the two types of data collected to assess a patient. They both provide information about the present state of the patient as well as his/her needs. Differentiating and knowing the importance of objective and subjective data is key in diagnosing and developing a health care or treatment plan for patients. With this in mind, let’s move on to defining objective and subjective data.
Objective Data
Objective data is information that can be obtained using our five senses. Results are products of our direct observations or measurement through laboratory tests, physical examination as well as taking vitals. They are verifiable and reliable. They give nurses insight into the care a patient would require and helps physicians make an official diagnosis. Examples of objective data include but not restricted to: pulse rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, ambulation, heart rate, body temperature, weight, wound appearance, demeanor, bleeding, Full blood count, blood urea and creatinine levels, as well as X-ray or computed tomography (C T) scans. With that understanding, let us move on to defining subjective data.
Subjective Data
Subjective data is information provided by the patients or their family members or caregivers. This is information patients give concerning how they feel, what symptoms they are experiencing, their fears, and concerns. Subjective data give insight into how susceptible a patient is to a health problem and the psychological as well as the physiological condition of the patient. They also confirm objective data.
Subjective data cannot be measured or verified by the nurse or physician; for example, a patient complains that she has frequently been vomiting for the past three days. It is objective because it cannot be verified. Other examples include Feelings, perception, ideas, desire or cravings, Sensations like itching, preferences, beliefs, values, and pain.
Among these examples, pain is the most important objective data; it is also referred to as the 5th vital sign, it indicates a problem that needs to be addressed fast. Although being subjective data cannot be measured or detected with a tool, patients can provide information on how severe their pain is when asked to rate it on a scale of 1 to 10, 10 being excruciating pain.
Now that we precisely know what objective and subjective data are, let’s discuss their differences.
Differences Between Objective and Subjective Data
You must have heard of signs and symptoms when discussing diseases. Symptoms are generally regarded as subjective while sigs are regarded as objective.
There are times that subjective and objective data occur simultaneously, for example:
- A patient complains about having a fever and the nurse observes that his temperature is very high
- A patient complains of persistent cough and the nurse observes her coughing all through the assessment
- A patient complains of shortness of breath and his oxygen saturation reading is observed to be low
There are occasions where objective and subjective data do not go together; a patient may express having certain symptoms and observations and lab test results may reveal something completely different. For example
- A patient may say he/she feel relax and calm but the nurse may observe high blood pressure readings
- A lady may say she feels she is pregnant and report that she is having all the symptoms of pregnancy, however, pregnancy test results may come out negative.
Let me further help you understand Objective versus Subjective data by analyzing two instances and separate the information provided into subjective and objective data.
Subjective vs Objective Instance: 1
A 20-year-old male patient complains of sharp stomach pain and feeling dizzy, his heart rate was observed to be 110 beats per minute, his abdomen was hard and distended, and dull short tones were heard while percussing over each quadrant. EKG results came out normal.
Now let’s sort this into subjective and objective data:

Subjective vs Objective Instance: 2
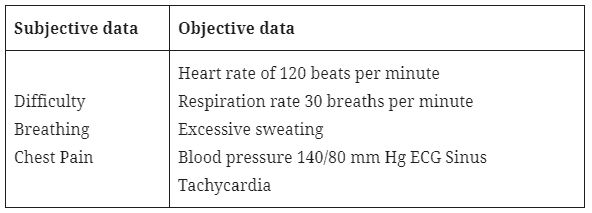
A 60-year-old female patient says she has difficulty breathing. The patient’s heart rate and respiration rate were observed to be 100 beats per minute and 30 breaths per minute respectively. The patient later complains of excruciating chest pain that feels like pressure. The patient is observed to be sweating excessively and pale. Blood pressure is seen to be 140/80 mmHg Electrocardiogram (ECG) shows Sinus Tachycardia.
Now let’s sort this into subjective and objective data:
Subjective vs Objective data, Which is more important?
Now that we know what objective and subjective data are and the role they play in evaluating a patient’s condition, which is more important?
The simple answer is both of them. Proper and accurate diagnosis, as well as the treatment of a patient, requires both objective and subjective data. Signs (Objective data), indicating a disease may be similar for many diseases, however, symptoms, that is, subjective data may provide clues on the specific illness a client may have. Hence, we can see that objective and subjective data work together to produce a clear picture of a patient’s condition.
In Conclusion:
It is evident that objective and subjective data, although different, they are equally vital in assessing a patient. While subjective data serve as the first attempt for medical professionals to establish a good relationship with patients and build trust as well as have an idea of a patient’s condition, objective data supported by medical laboratory test reports, physical examinations, CT scan, Electrocardiogram (ECG) and so on, provides conclusive results.
Also read How To Become An Emergency Room(ER) NURSE